TCFD
Based on the four aspects of the TCFD (Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures), we are gradually building a resilient climate governance framework and information disclosure system. At the governance level, the Board of Directors provides the highest level of oversight for climate change issues and is responsible for regularly reviewing the Company’s overall sustainability strategy and risk management approach. In addition, we recognize the significant impact of climate change on the Company’s long-term operations and sustainable development and are actively adopting the risk management framework proposed by the TCFD. We also reference the guidelines of IFRS S2 on climate-related disclosures in systematically identifying and assessing the risks and opportunities that climate change may pose to the Company’s operations and finances.
| TCFD Aspect | Contents |
|---|---|
| Governance | The Company has established a "Sustainability Promotion Team", led by the CFO, to coordinate and oversee the advancement of climate-related initiatives. The task force regularly reviews the implementation of climate-related issues annually and reports to the Board of Directors for review, ensuring that climate risks and opportunities are integrated into the Company’s core governance framework and are aligned with the overall sustainability information management system. The Board of Directors, as the highest supervisory body for climate-related issues, is responsible for resource allocation, disclosure decisions, and driving progress towards goals, ensuring climate action aligns with the Company’s strategic direction. |
| Strategy | We are committed to addressing climate risks and capitalizing on the opportunities presented by the transition to a low-carbon economy. We actively promote carbon reduction initiatives with specific actions as we navigate an orderly transition. These include the adoption of green and low-carbon processes, strengthened energy conservation management, optimized energy efficiency, the development of low-carbon and microbial application products, and the introduction of a circular economy in relation to raw materials. We continuously strengthen our circular economy and green operations systems. We are concerned about the potential financial impacts of extreme climate events on operations, asset valuation, and capital costs. For this reason, we continuously enhance overall corporate adaptability and operational resilience through institutional design and risk management mechanisms. |
| Risk Management | The Company adopts the TCFD framework to identify climate-related risks and opportunities, analyze their potential impact on operations and finances, and prioritize and develop countermeasures based on timing and severity to strengthen adaptation and transition resilience. The Company's risk management system employs a dual approach of top-down implementation and cross-functional integration. Each business unit is responsible for regularly identifying changes in risks related to operations, finance, the environment, climate, and hazardous events. Senior management is responsible for establishing risk management policies and operational structures, and implementing corresponding strategies according to Board of Directors’ decisions. The Company reports on the execution of risk management to the Board of Directors annually. |
| Metrics & Targets | We have been planning to set specific indicators and quantifiable targets for climate change risks and opportunities, based on the TCFD framework, to serve as the basis for future internal management and performance tracking. We will continue to review the appropriateness of indicators and targets, and gradually reduce the impact of our operations on the environment through strengthened energy and resource management and improved waste recycling efficiency. |
Climate Change Risk and Opportunity Management
| Risks / Opportunities | Category | Description | Impact | Impact on Finance | Management Measures |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Risks | Physical | Increased severity of extreme weather events, such as typhoons and floods | Damage to crops, disruptions to production and supply, and impacts on product delivery and market availability | Increased repair costs, business interruption losses, and rising insurance premiums |
|
| Changes in precipitation patterns and extreme climate shifts | The unstable crop growth environment affects the accuracy of the performance and demand forecast of fertilizer products | Fluctuations in market demand lead to increased costs for inventory management and production scheduling adjustments |
|
||
| Transformation | Cost of low-carbon technology transformation | If the speed of transformation does not keep pace with market demand, it will affect product competitiveness and opportunities for customer collaboration | Increase in R&D costs, impacting profitability (short term) |
|
|
| Changes in customer behavior | Customers’ increasing demand for low carbon and eco-friendly products will lead to loss of market share if not addressed | Decreased sales and damage to brand image |
|
||
| Opportunities | Products & Services | New low-carbon products and new climate adaptation solutions (mid-term) | Satisfy the market demand for low-carbon, climate-resilient agricultural technologies and generate new revenue streams | Develop new product markets and diversify the revenue structure |
|
| Resource efficiency | Recycling and reuse of agricultural waste | Reduce the burden on the environment to enhance the resilience of agricultural ecosystems | Reduce the cost of raw material procurement, lower waste disposal costs, and improve overall operating efficiency and gross profit margin |
|
Energy and GHG Management
Energy Management and Usage
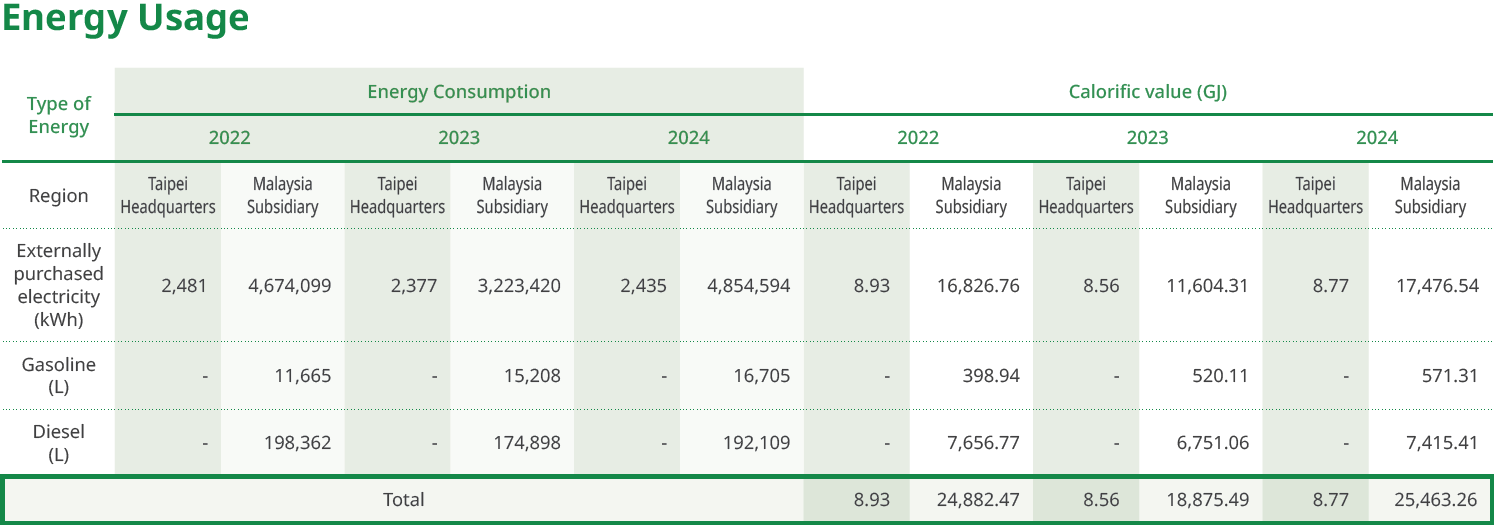
At present, the Company’s primary energy consumption is electricity used in product manufacturing, representing roughly 68.63% of its total energy use. This electricity consumption is sourced from usage reported on electricity bills. Diesel fuel accounts for roughly 29.12% of total energy consumption and is used in transportation equipment such as forklifts and company vehicles, with sourcing based on amounts listed on oil procurement invoices. The Company currently does not utilize renewable energy or generate its own power. No energy was sold in 2024. We value the efficient use and continuous improvement of energy, and consider energy conservation a key strategy for both environmental protection and operational efficiency. We are also actively assessing the feasibility of adopting solar power generation systems, with the goal of gradually reducing our dependence on non-renewable energy sources, thus achieving energy diversification and a reduction in carbon emissions.

GHG Management
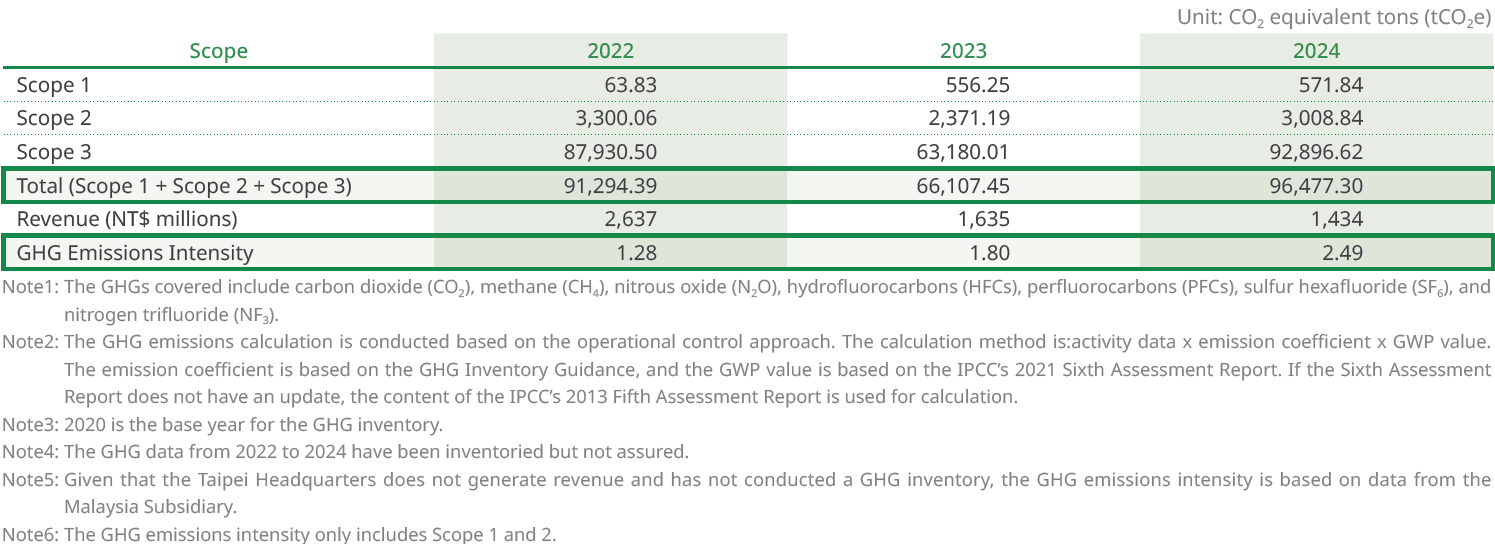
In response to global climate change trends, we are actively aligning with Taiwan's 2050 Net-Zero Pathway and Strategies released by the National Development Council, and the Financial Supervisory Commission’s “Roadmap for Sustainable Development of Listed Companies”, to enhance the organization’s climate risk resilience. Meanwhile, to support Malaysia's carbon neutrality policy, we initiated organizational-level GHG inventories in 2020 and have concurrently developed a phased plan for carbon reduction strategies.
Carbon Reduction Initiatives at the Malaysia Subsidiary
According to the results of the GHG inventory, over 90% of carbon emissions come from materials (particularly chemical raw materials) and their logistics and transportation. In addition, the Company refers to the climate policies of by the Malaysian government as the basis for its operational planning, including the goals of reducing carbon emissions by 45% relative to GDP by 2030 and achieving net-zero by 2050. In order to effectively respond to the carbon reduction challenges, ACBT has launched three carbon reduction initiatives:

Water Resource Management
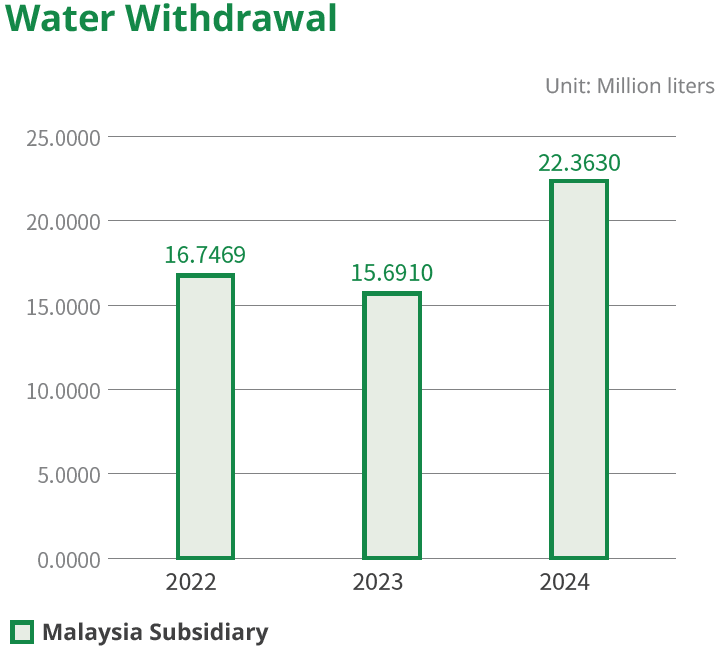
The water resources for the entire facility are sourced from municipal water, primarily for use in daily factory operations. According to the World Resources Institute (WRI) Aqueduct Water Risk Atlas, the overall water stress in the area where our Malaysia office is located (Johor Bahru) is "Low (0–1)",
while in Taipei City, where our headquarters is located, it is "Low - Medium (1–2)". Water stress is relatively low at both operating locations. Although our production processes require less water than other industries, we still view water resources as essential to our operations and are committed to responsible water usage, ensuring operational efficiency and environmental protection go hand in hand. To improve water efficiency, we have implemented basic water recording and monitoring systems, and are continuously tracking water usage trends to assess the potential for future water conservation and reuse initiatives. In addition to water intake, a rainwater harvesting system is also in place for water conservation. While the current system is relatively simple and only allows for limited rainwater recycling, it still effectively supports landscaping and irrigation within the factory area, reducing reliance on municipal water.
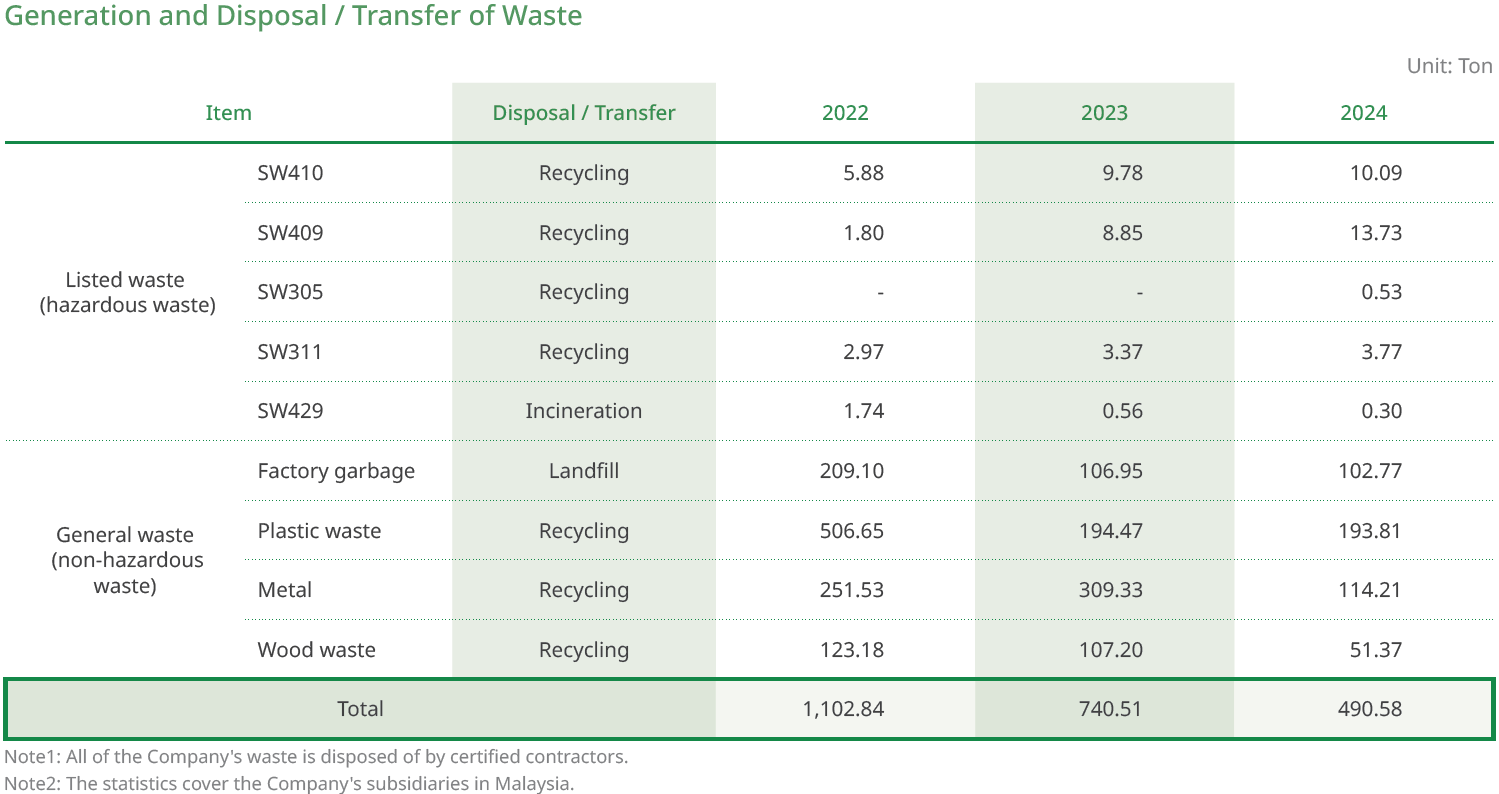
Waste Management
We are committed to implementing green manufacturing practices, viewing waste as an integral part of the resource cycle, and establishing a comprehensive classification, tracking, and compliance management system to ensure proper handling and maximize the reuse of all waste generated during operations. The Taipei Headquarters primarily handles stock affairs and is not involved in any physical development or manufacturing, eliminating concerns about pollution or waste generation. Resource recycling bins are available on each floor for waste sorting and recycling, and employees are expected to comply with resource recycling guidelines to promote environmental protection. The manufacturing processes of the Company’s Malaysia Subsidiary comply with the classification and management requirements of the Environmental Quality Act 1974 and the Environmental Quality (Scheduled Wastes) Regulations 2005. All 77 types of waste listed in the Regulations are classified as controlled waste, with all others being non-controlled waste. In 2024, the Company generated five types of regulated waste from its operating activities.
ACBT maintains complete records and tracking of the generation and treatment of various types of waste to ensure information traceability and process auditability. For controlled waste, shipping notes in standard format are used as required by government regulations. These notes detail the waste category, weight, source, treatment method, and time, and are submitted by third-party treatment contractors holding valid environmental permits. This management system can effectively prevent potential environmental risks, and also assists in establishing waste reduction goals and evaluating overall treatment efficiency, as well as facilitating inspections by regulatory authorities and annual audit requirements.